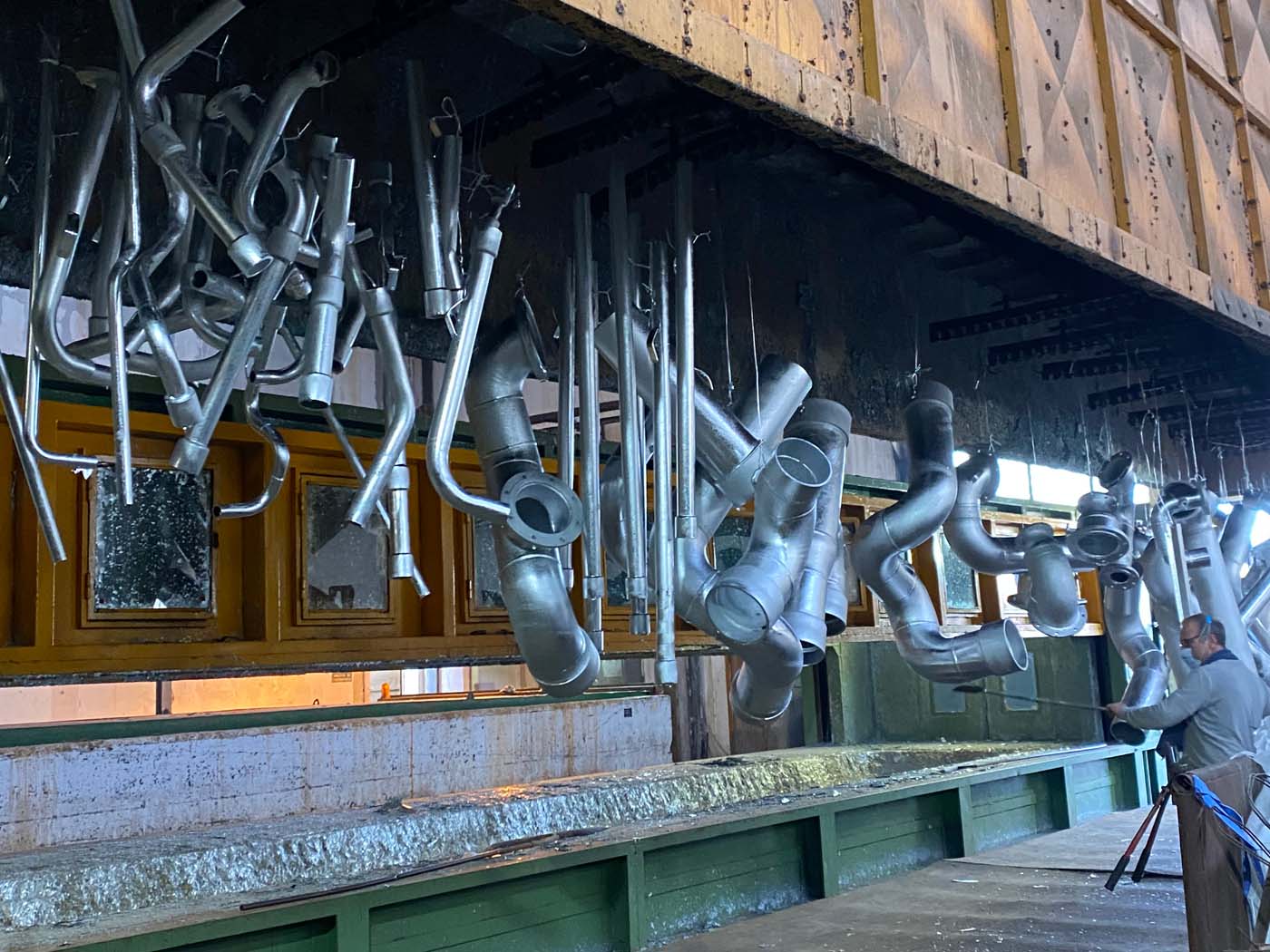
HOT DIP GALVANIZING
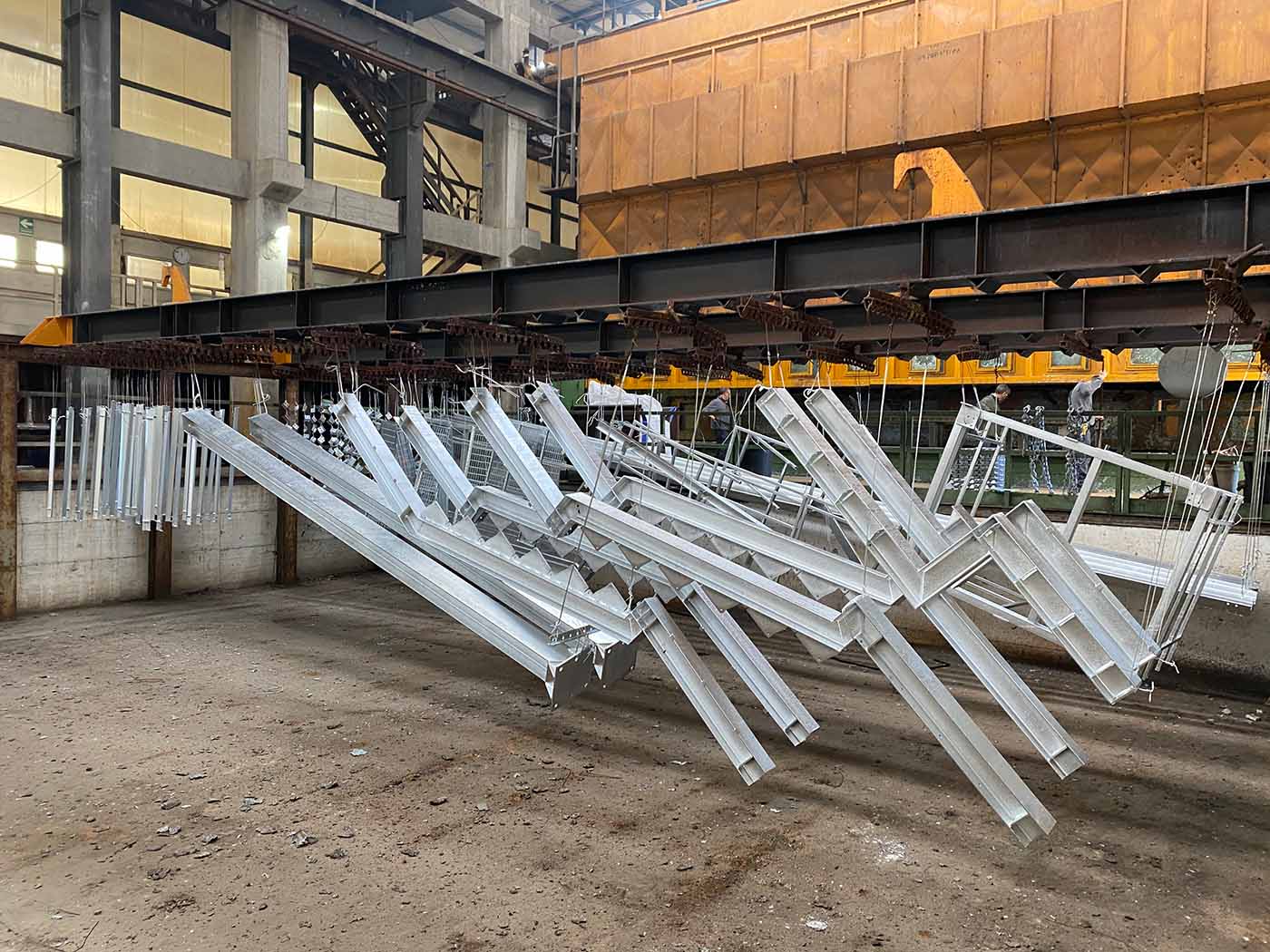
Hot-dip galvanizing is the best corrosion protection process for metal products.
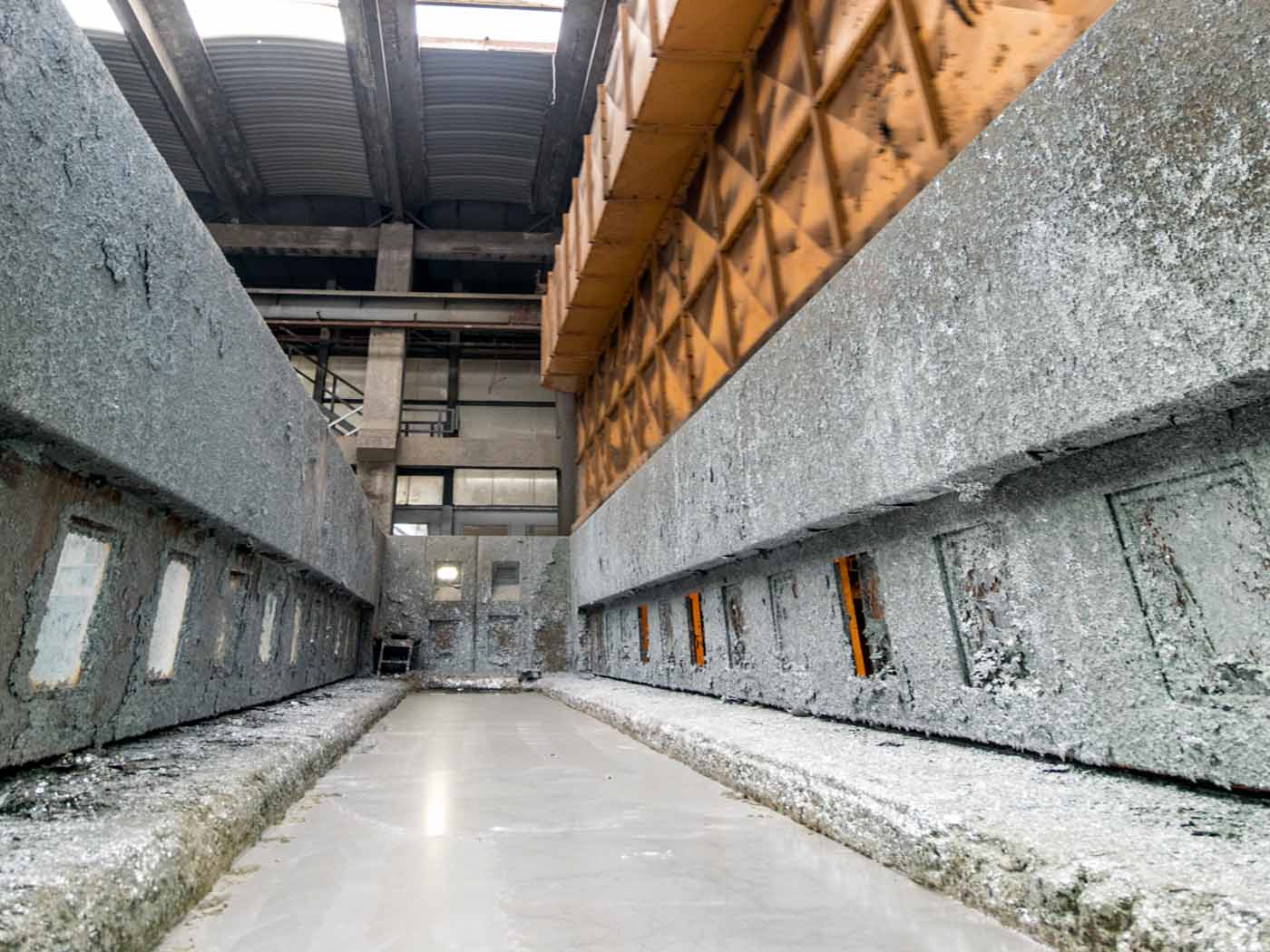
The protective coating is obtained by immersing the products in a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of about 450°C and ensures the best performance in terms of adhesion of the coating to the substrate since a real alloy takes place between zinc and steel (formation of continuous layers of Fe-Zn alloy).
Galvanized steel is the emblem of the circular economy in the construction sector. Hot-dip galvanizing, avoiding the corrosion of the steel, lengthens the useful life of the structure, drastically reduces maintenance and facilitates reuse.
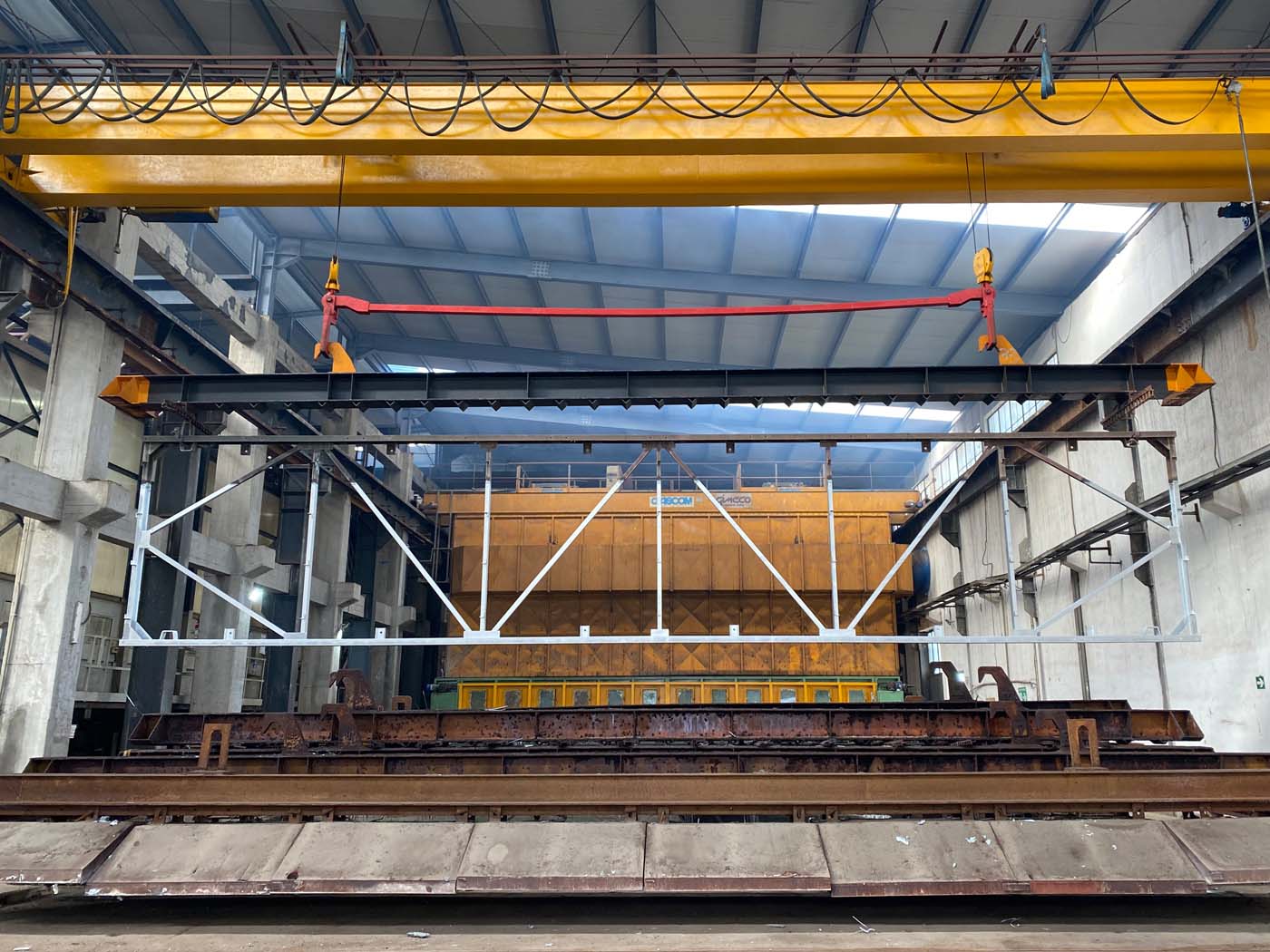
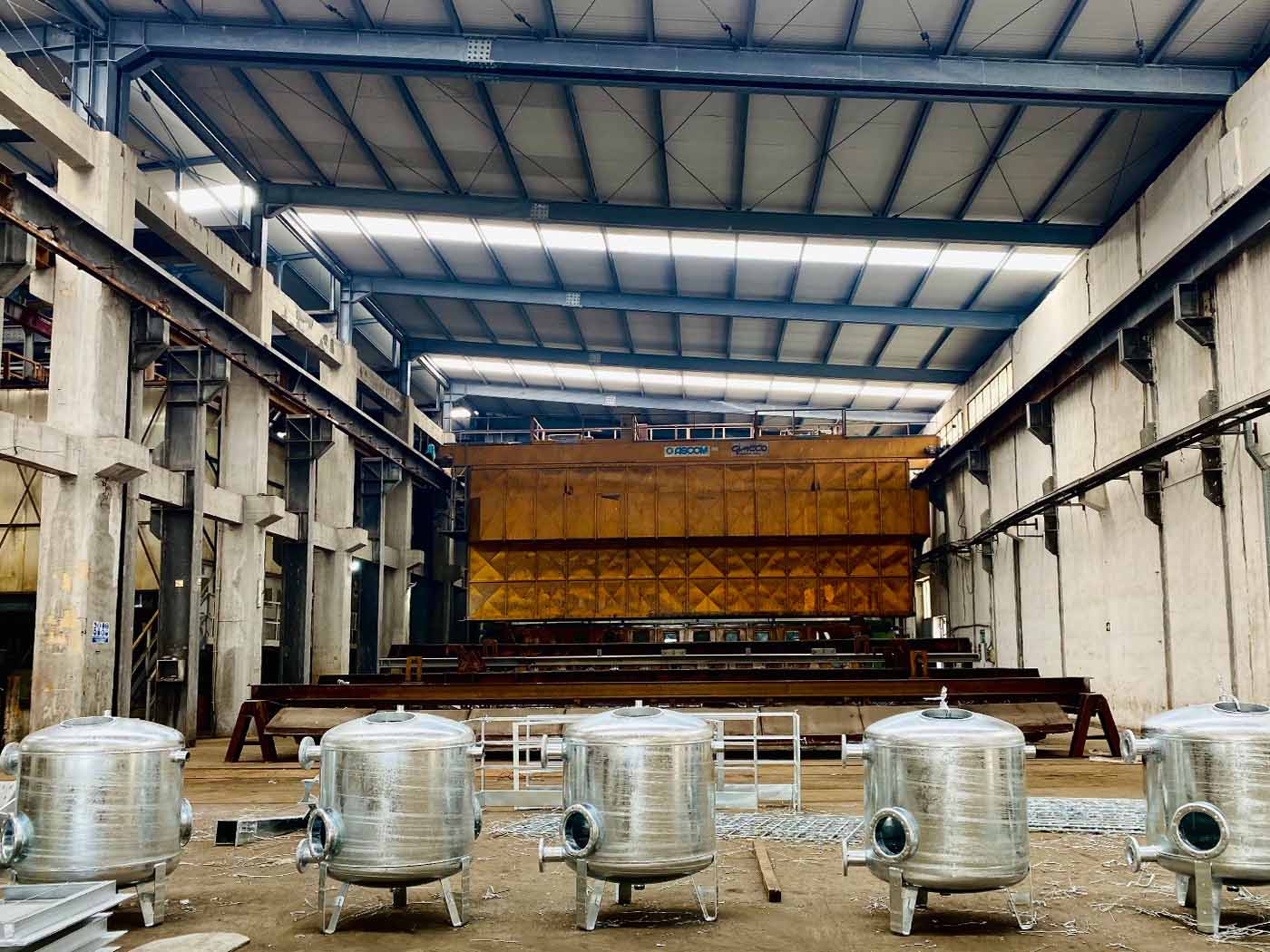
Our plant allows you to galvanize products with maximum dimensions of 12.500 x 1.430 x 2.600 mm.
We also offer the covered storage service, testing and adhesion test of the coating.
Tecnozinco operates according to the highest quality standards guaranteeing a proven HiQualiZinc quality. The checks are carried out according to the UNI EN ISO1461 technical specification.
The best techniques available are applied in the production process to minimize environmental impact.
UNI EN ISO 14713 Standard provides information and the right preparations needed to properly proceed with hot dip galvanization process.
Here follows some advices useful in designing and working phases.
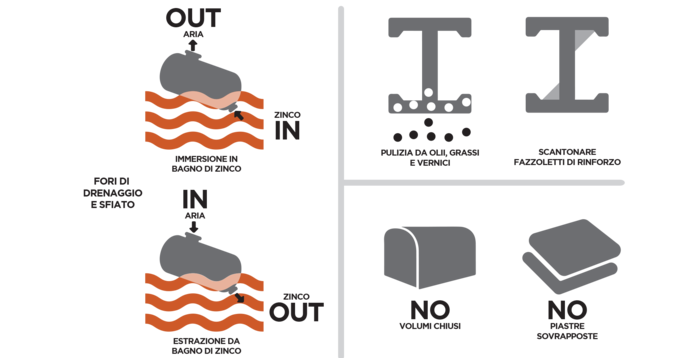
1
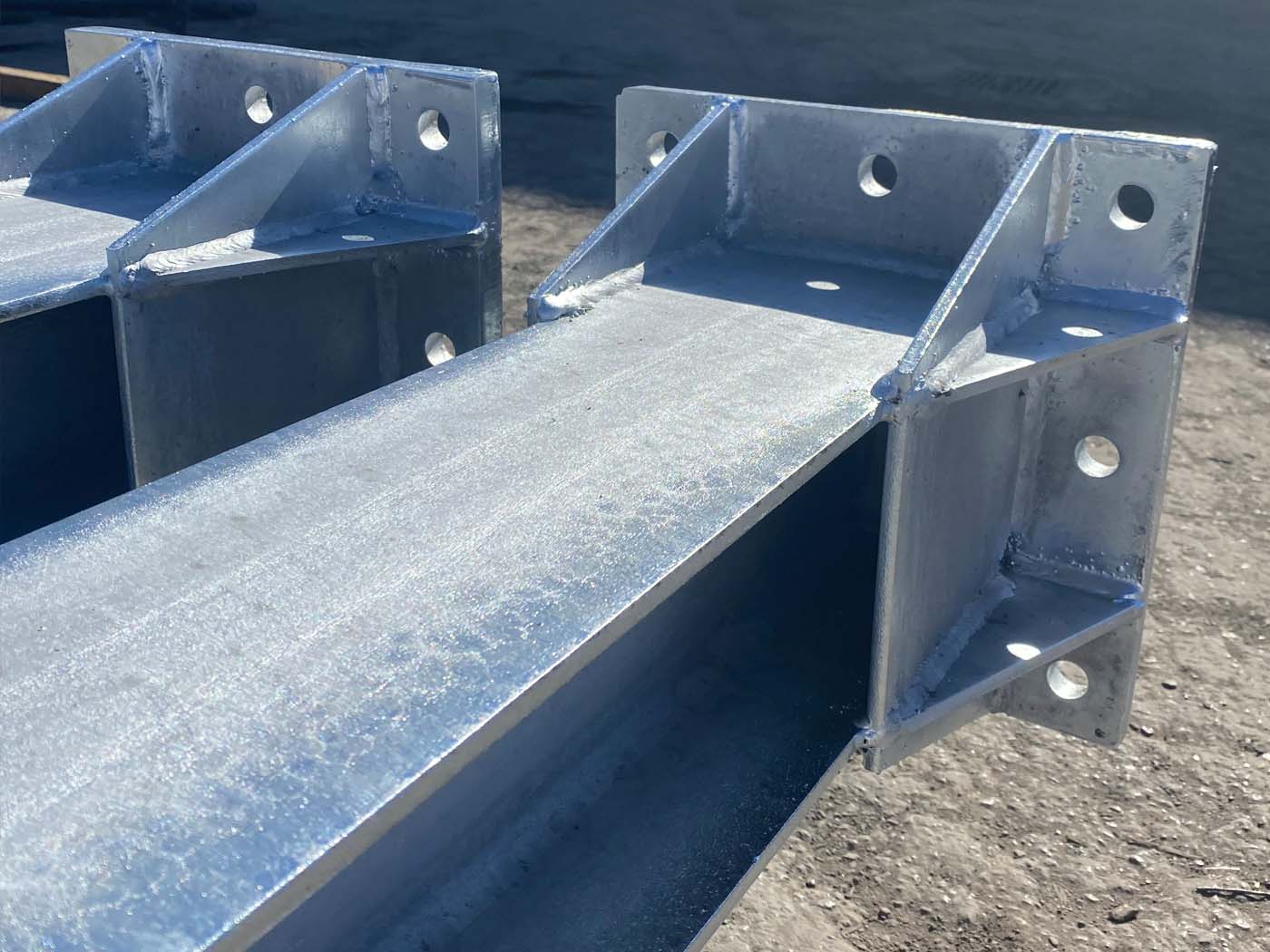
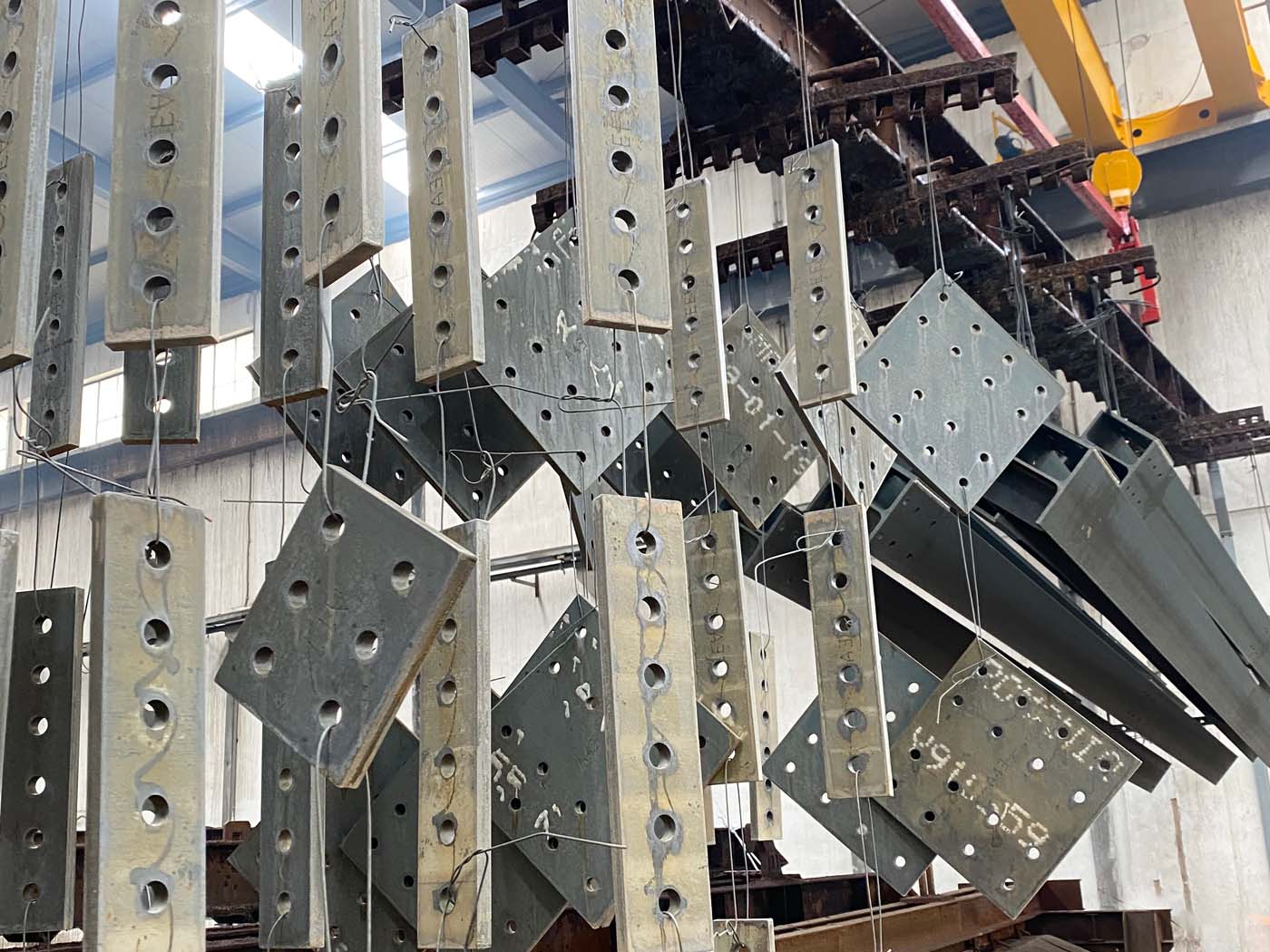
Reinforcement plates must be properly notched in the corners to let the process fluids drain during the galvanization process.
2
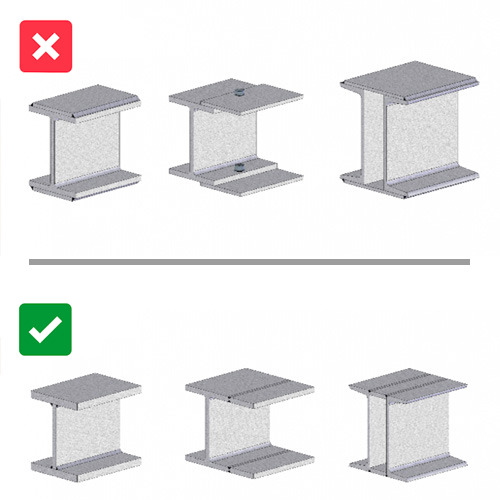

Plate overlapping should be avoided in order to avoid defects caused by process fluids infiltration.
3
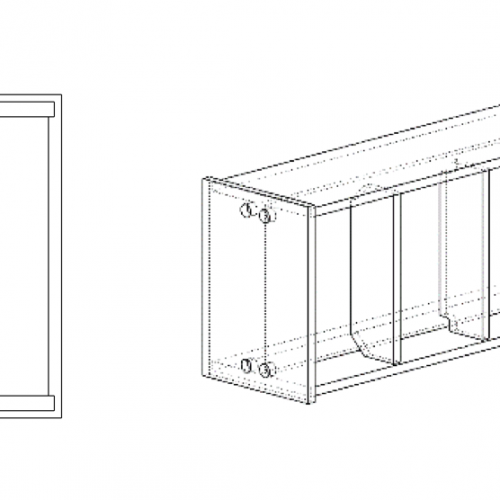
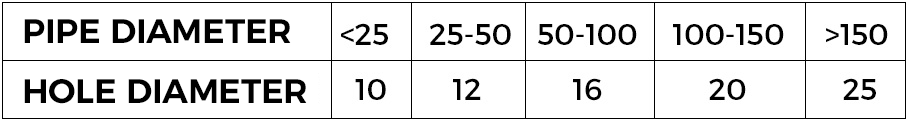
Ventilation holes must be properly dimensioned to ensure the correct galvanizing for pipes and avoid process fluids stagnation.
(table in mm)
4
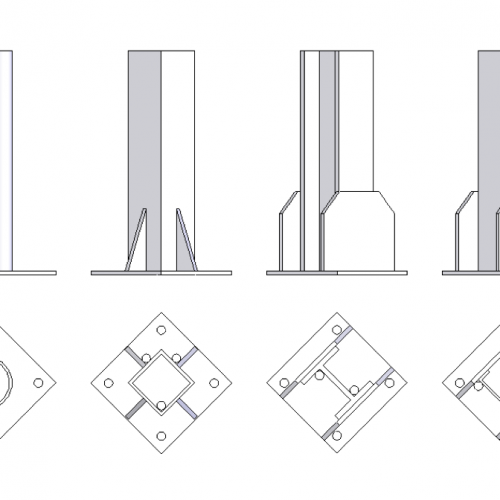
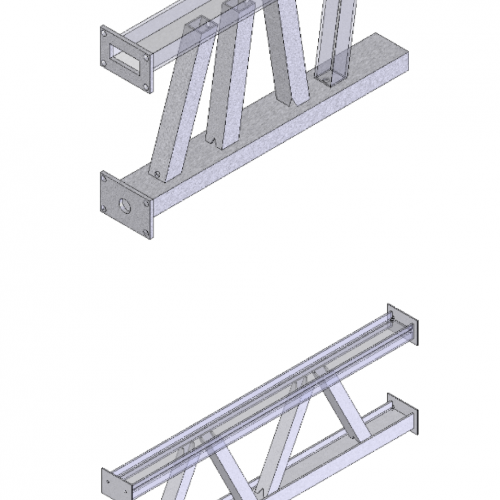
There are many methods to make the ventilation holes on beam with base plate. Here some examples of ventilation holes good enough to avoid notching reinforcement plates.
5
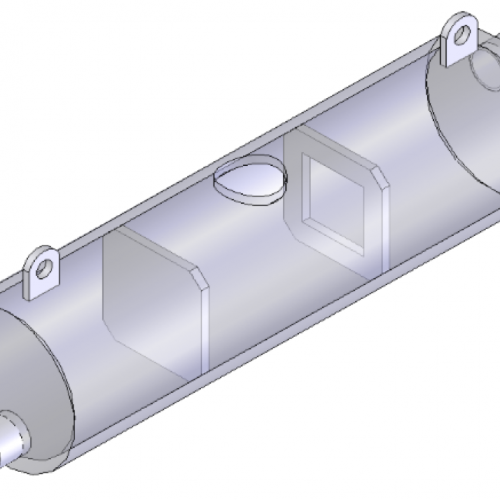
For reinforcement plates in big dimension products, central holes or notching must be considered in advance properly placed and oriented. Load anchoring system also must be considered in advance.
6
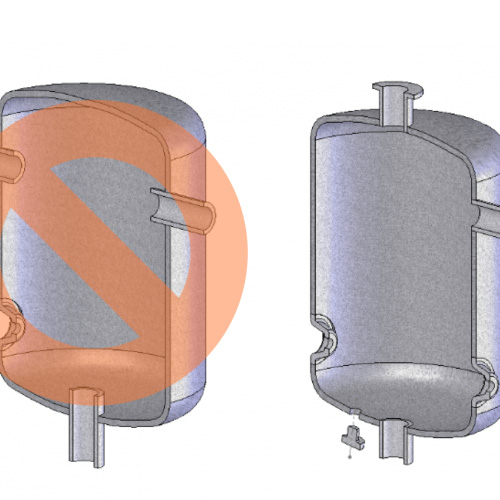
In steel tanks the connection pipes must be designed properly to avoid process fluid stagnation.
FAQ
No: the process is carried on by dipping entire products into molten zinc bath. It’s possible to cover small areas (threads for example) using adequate anti-zinc coating but degrading the final result.
No: the air into the pipes block the dipping into molten zinc and incorrect ventilation hole positioning can cause major damages to the products and major accident to workers and machineries.
Despite the bigger starting cost comparing to other solutions, considering the entire product life cycle assessment the money saving is glaring, in fact is the most used solution for public government constructions.
YES: There are many primers ready to be painted on galvanized surfaces that ensure the anchor of the painting layer to galvanized steel. This kind of surface treatment known as “duplex” gives a better protection than the sum of the singles treatments. Moreover, painting galvanized surfaces can be useful when particular aesthetic effect is required.
So called “cold galvanization” process is not a galvanization process but a simpler painting process performed using high zinc content paintings. There is no alloying reaction during this process and the result is just an exterior layer that perform a basic protection against corrosion not even remotely comparable to hot dip galvanization results.
Increase of weight is about 3% to 10% depending on chemical composition of the treated steel and on shape and dimension of products. It’s good thing consider the increasing of weight during design process.
Zinc bath dimensions are: 12,50m x 1,50m x 3,00m; maximum processable dimensions in single dip are: 12,00 x 1,44 x 2,70 m
Protection duration provided by hot dip galvanization process is strictly connected to the environment where products are positioned during their life cycle. To define the duration is needed first to identify the Environment Corrosivity Class.
UNI EN ISO 14713-1 Standard express for each class the corrosivity rate in µm/year:
Environment corrosivity class | Environment description | Thickness decline |
C1 | Inside heated buildings with a clean atmosphere, for example offices, shops, schools, hotels. | ≤ 0.1 |
C2 | Environments with a low level of pollution. Especially natural areas. | da > 0.1 a 0.7 |
C3 | Urban and industrial environments. Modest sulfur dioxide pollution. | da > 0.7 a 2.1 |
C4 | Industrial areas and coastal areas with moderate salinity. | da > 2.1 a 4.2 |
C5-I | Industrial areas with high humidity and aggressive atmosphere. | da > 4.2 a 8.4 |
C5-M | Coastal and offshore areas with high salinity. | da > 4.2 a 8.4 |
lm-1 | Immersion in fresh water. | 20 |
lm-1 | Immersed in brackish or sea water. | da 15 a 25 |
By dividing alloy thickness value to annual thickness loss, the result show the number of years durability: 40 – 120years.
This event known as “white rust” is caused by zinc oxidation and it’s considered into reference standard. Moist atmosphere catalyze production of zinc hydroxide, oxide and carbonate in Steel products that just ended galvanization process; all these products doesn’t affect natural protection ensured by zinc layer.
YES: after studies carried out by Corrosion Department of Marche Engineering University it was proved that hot dip galvanized rebar adhesion on concrete is superior than not galvanized rebar. By galvanizing rebar is also prevented the well-known issue of reinforcement covering detachment and the following rebar exposure, typical in most of the reinforced concrete structures.
OUR SERVICES
SANDBLASTING
PAINTING
TRANSPORT
THICKNESS TESTING
ADHERENCE TEST
















